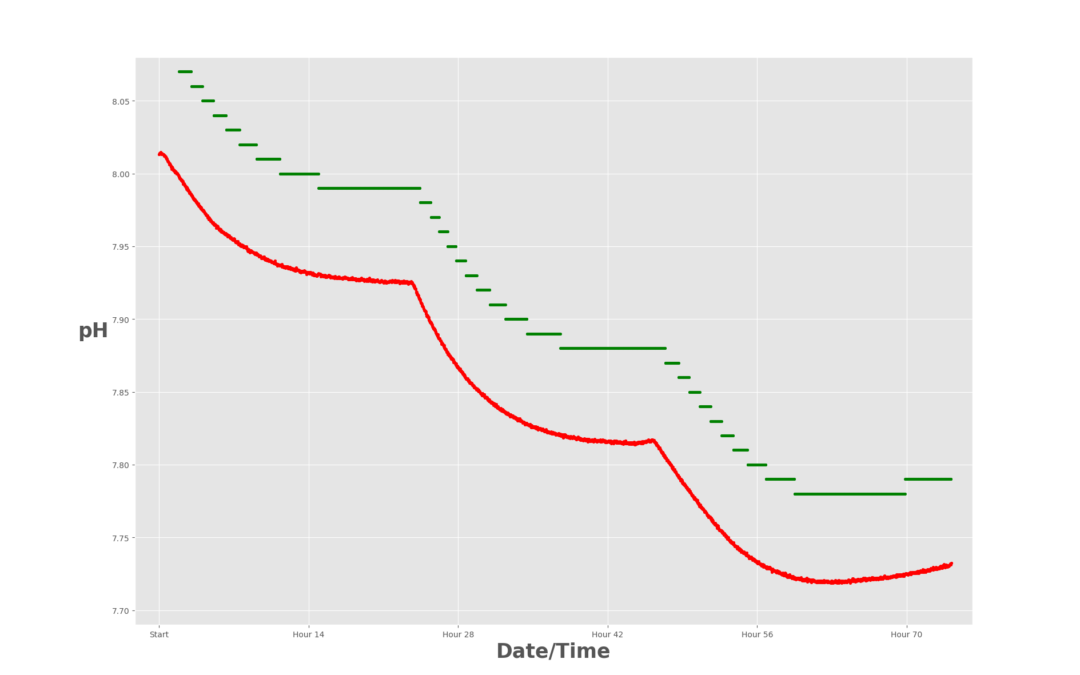
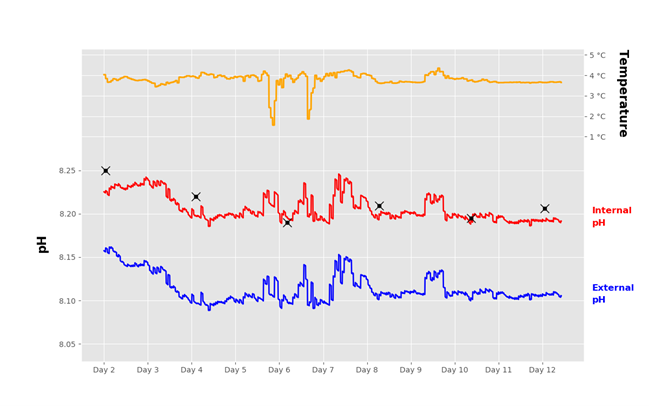
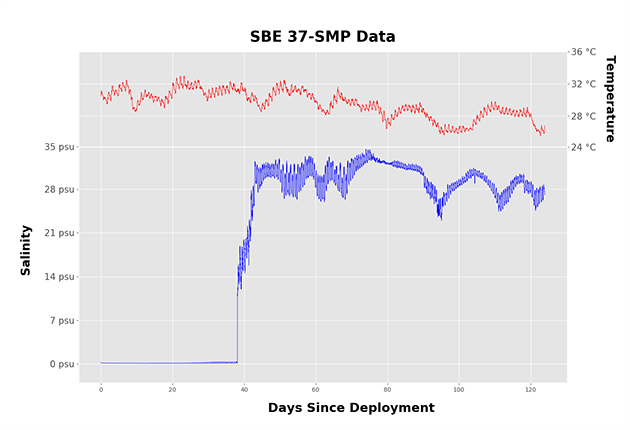
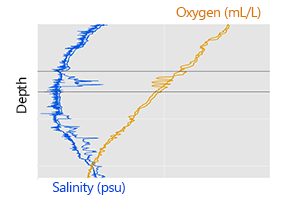
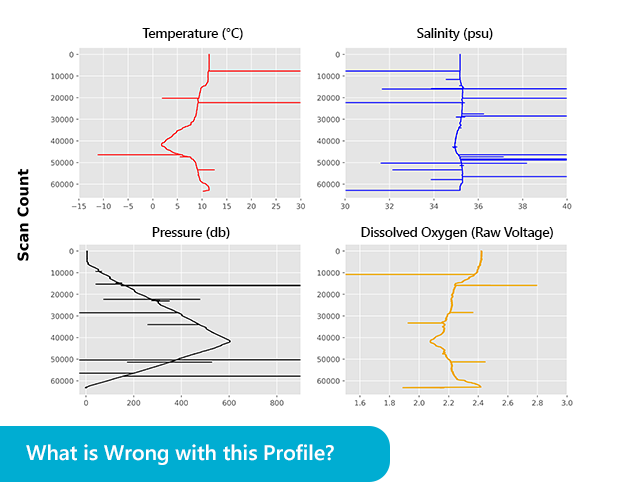
January 2019 Newsletter The data shown above originate from two different pH sensors deployed in the same well-mixed test bath. Both sensors were cleaned, tested, and calibrated before deployment, and were given 24 hours to equilibrate before recording data. So why...